Gurgaon, once a village associated with Guru Dronacharya, the revered teacher of the Kauravas and Pandavas, has a rich history influenced by various rulers. During Akbar’s reign, it was part of Delhi and Agra’s territories. In the early 19th century, the British established control over Gurgaon, initially monitoring Begum Samru’s forces. After the 1857 revolt, Gurgaon was moved from the North-Western provinces to the Punjab province.
In 1966, Gurgaon became part of Haryana when the state was formed. Until the 1980s, it was largely agricultural, serving as Delhi’s peaceful green backdrop. The transformation began with Maruti Udyog’s manufacturing unit in the late 1970s and Hero Honda’s plants, followed by DLF’s real estate developments in the 1980s. HUDA and licensed colonisers played a role in urbanisation, turning Gurgaon into a thriving satellite city in the National Capital Region (NCR), earning it the title of the ‘Millennium City.’
However, this rapid development has resulted in disparities, with underdeveloped villages facing infrastructure challenges due to rapid population growth. There is a need for more inclusive and equitable development effort in the district.
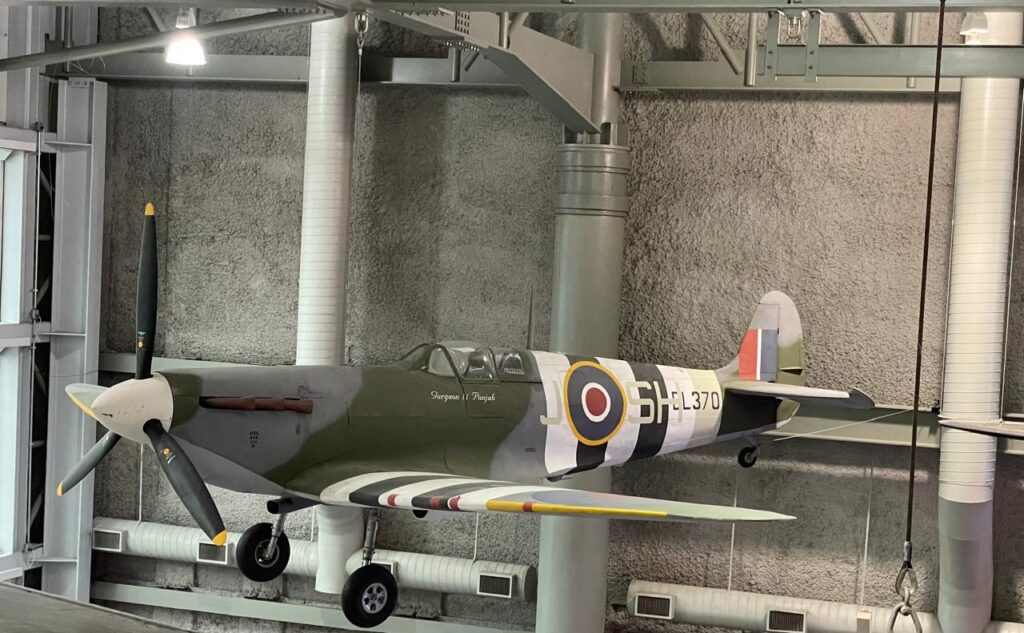
A Memorabilia!!
Below the canopy of this World War II fighter plane in a museum in New Orleans in US, is written Gurgaon-Punjab!

The Gurgaon District at a Glance
| Area | 1258 sq. km |
| Population | 15,14,085 * |
| Population growth rate | 79.93% |
| Literacy Rate | 84.4% |
| Sex Ratio | 853 females per 1000 males* |
| Sub Divisions | 4 |
| Development Blocks | 4 |
| Revenue Tehsils | 5 |
| Revenue Estates | 291 |
| Villages | 193 |
| Urban Local Bodies |
*Source: 2011 Census
Fact File
- Gurgaon is a major suburb in the National Capital Region of Delhi, ranking as the second-largest city in Haryana.
- It shares borders with Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Delhi, making it strategically located.
- Gurgaon district contributes significantly to Haryana’s economic prosperity, with 25.3% of the state’s GDP and the highest per capita income.
- The city boasts excellent connectivity through the Delhi-Jaipur-Ahmedabad rail link and NH 8, attracting people for work, travel, and entertainment.
- Gurugram city (tehsil) is governed by a Gurgaon Municipal Corporation that elects one councilor for each of its 36 wards.
- Gurgaon is known for its modern infrastructure, including office towers, apartment complexes, cyber parks, hospitals, educational institutions, and commercial malls.
- The district land features include diverse terrain, with hills in the southeast, sand dunes in the northwest, and seasonal streams. Gurgaon lacks perennial rivers. It experiences extreme temperatures and limited rainfall, posing environmental challenges.
- Population density has notably increased in Gurgaon tehsil and central Gurgaon city due to high urbanisation rates. Demographic changes driven by industrialisation, infrastructure development, and the IT sector have led to significant population growth.
- Agriculture in Gurgaon: In 1991, 53.9% of workers were engaged in agriculture, but by 2011, it decreased to 12.3%. Groundwater irrigation is crucial for agriculture, although the cultivated land area has reduced from 656.23 sq km in 2007 to 515.59 sq km in 2017.
- Industry in Gurgaon: Gurgaon is a major industrial hub, especially in the automobile industry, housing Maruti Suzuki, India’s largest car company. Other industries include telecommunications, electrical goods, sports goods, rubber products, garments, and software development. Tertiary activities like IT, software, services, and sales now dominate the economy, constituting 81.4% of the main workforce. The district is a stronghold for IT and BPO companies, with the third-highest per capita income in India. Over 250 Fortune 500 companies operate in Gurgaon, solidifying its status as a key economic hub.
- Master Plans: Gurgaon has had three master development plans for the years 2021, 2025, and 2031. These plans aim to create a strong economic foundation for future growth, improve transportation networks, develop infrastructure, plan land use efficiently, and promote sustainable development.
- Master Plan 2021: Released in February 2007, it anticipated a population of 27 lakhs and a density of 80 persons per acre. The plan was later revised in Master Plan 2025, increasing the density to 120 persons per acre. Initially, a large area was marked for a Special Economic Zone (SEZ), but it was dropped due to lack of interest.
- Gurgaon Manesar Urban Complex 2031: Released in November 2012, it caters to a projected population of 42.5 lakhs. The plan continues the focus on balanced development and sustainable growth for Gurgaon’s future.
Download link: Gurgaon Manesar Urban Complex -2031
Administrative Structure
The district is divided into five revenue tehsils, four sub-tehsils, and four rural development blocks. There are two municipal corporations within the district, Municipal Corporation of Gurgaon and Municipal Corporation Manesar. There are a total of 193 villages and 162 panchayats in Gurgaon district.
The Deputy Commissioner is the Chief District Officer of the Gurgaon Administration. He is assisted by Sub Divisional Magistrate heading a subdivision. The CEO Zila Parishad is in-charge of District Rural Development Agency (DRDA) for development of the district. Sectoral development is looked after by the district head of each development department such as agriculture, animal husbandry, health, Education etc. Administrative Structure snapshot
| Tehsils (5) | Gurgaon, Sohna, Pataudi, Farrukh Nagar, Manesar |
| Sub-Tehsils (4) | Wazirabad, Badshahpur, Kadipur, Harsaru |
| Blocks (4) | Gurgaon, Sohna, Farrukh Nagar, Pataudi |
| Municipal Corporation (2) | Municipal Corporation Manesar, Gurugram Municipal Corporation, |
| Municipal Council (2) | Sohna, Pataudi Mandi |
| Municipal Committees (1) | Farrukh Nagar |
| Total Villages | 193 |
| Total Panchayats | 162 |
| Village Level | Panchayat (162) |
| Block Level | Panchyat Samiti (4) |
| District Level | Zila Parishad (1) |
| Block | No. of Villages as on Feb. 2021 | No. of Panchayats as on February,2021 |
| Total | 193 | 162 |
| Gurgaon | 11 | 10 |
| Sohna | 47 | 33 |
| Pataudi | 87 | 73 |
| Farrukh Nagar | 48 | 46 |
| Sub Divisions (4) | Gurugram, Sohna, Badshahpur & Pataudi |
| Tehsils (5) | Gurgaon, Sohna, Pataudi, Farrukh Nagar, Manesar |
| Sub-Tehsils (4) | Wazirabad, Badshahpur, Kadipur, Harsaru |
| Blocks (4) | Gurgaon, Sohna, Farrukh Nagar, Pataudi |
| Municipal Corporation (2) | Municipal Corporation Manesar, Gurugram Municipal Corporation, |
| Municipal Council (2) | Sohna, Pataudi Mandi |
| Municipal Committees (1) | Farrukh Nagar |
MP’s and MLA ‘s of Gurgaon
- Rao Inderjit Singh, BJP is the current Member of Parliament.
- Sudhir Kumar Singla, BJP is the Member of Haryana Legislative Assembly from Gurgaon while Rakesh Daultabad (Independent) is the Member of Haryana Legislative Assembly from Badshahpur.